When specifying laser modules, wavelength selection is key to the success of your application. In some cases, the application itself demands a specific wavelength. In others, expert wavelength selection may present opportunities to deliver a more cost-effective laser module solution. This excerpt from our “Successful Laser Module Specification” whitepaper discusses the importance of wavelength selection with application examples. Download the whitepaper for more information.
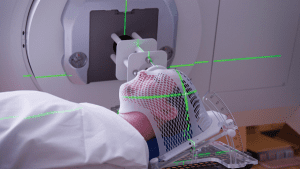
Laser diode wavelength selection
Central to laser module design is the selection of the right laser diode for the specific application and one of the first considerations in this selection process is laser diode wavelength. In some applications, such as patient positioning in medical or dental equipment, targeting for security, and industrial alignment operations, the laser will be viewed by the human eye. For these types of applications, green laser modules are preferred (e.g. at 520nm) as the human eye is more sensitive to green light than to other colors.
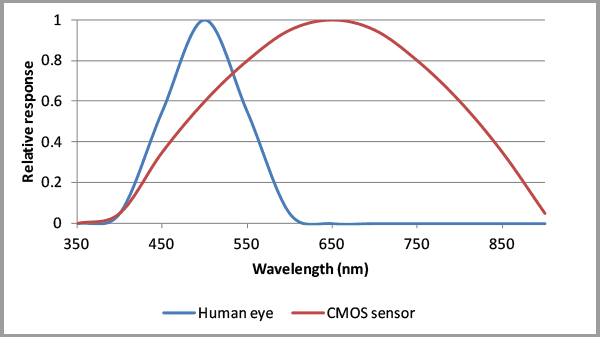
In applications where lasers are paired with cameras, such as shown in the chart above, most machine vision cameras are more sensitive to red light at around 650nm. For these applications, a red laser module may be most appropriate. Where invisibility is an advantage, for covert operations in security applications or for eye safety reasons, infra-red lasers are typically selected. In addition, newer model cameras used in machine vision applications are increasingly sensitive in the NIR (near-infrared). Other sensors are wavelength-specific or may be paired with optical filters to reduce the effect of daylight or artificial light, either for observation by the human eye or where a camera is used.
Specific Wavelengths – Laser Module Applications
In applications such as biomedical analysis, fluorescence or sorting, where materials being tested or analyzed respond only to light of a very specific color including 450nm or 488nm, lasers of those individual wavelengths offer performance advantages. A range of wavelengths may be essential for color mixing applications; for example, in RGB (red/green/blue) projectors.
Volume/ Cost considerations
Laser diodes used in high quantities, for example in consumer or telecoms applications, are typically lower-cost devices. These include 405nm blue-violet lasers for Blu-ray, red for optical disc drives, and near IR for laser printers or telecoms. When specifying a laser for a more specialized application there may be a significant cost benefit in selecting a wavelength commonly used in high-volume applications. For any application, it is important to understand the range of suitable wavelengths and not to restrict wavelength selection without proper analysis.
Learn more with our Successful Laser Module Specification Whitepaper
Wavelength selection is a critical first step in laser module specification. Understanding other elements of laser module selection including output power specification, thermal management, mechanical aspects, and electronics will help you to maximize the performance of your laser module. To learn more about specifying laser modules for your application, download the new whitepaper from the industry leaders at ProPhotonix. In “Successful Laser Module Specification”, ProPhotonix’ laser engineers, provide an expert guide, highlighting key criteria and trade-offs to ensure successful specification. With more than 25 years of experience providing OEMs with tailored laser modules, ProPhotonix has developed a 7-element approach to successful laser module specification.
The “Successful Laser Module Specification” Whitepaper details:
- Wavelength Selection
- Output Power Considerations
- Optical Design
- Thermal Management
- Mechanical Aspects
- Drive Electronics
- Partner selection
To learn more, Download the “Successful Laser Module Specification” whitepaper now.